Motor Disabilities
Types of Motor Disabilities
Traumatic Injuries
The key principle of web accessibility for users with motor disabilities is Operable, because not everyone can use a mouse, click on small links, or operate dynamic elements effectively.
Spinal cord injury
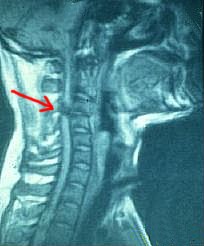 Spinal cord injuries can paralyze the limbs. Paralysis of the legs is called paraplegia. Paralysis of the legs and arms is called quadriplegia.
Spinal cord injuries can paralyze the limbs. Paralysis of the legs is called paraplegia. Paralysis of the legs and arms is called quadriplegia.
- Average age at injury is 31.7 years.
- Males account for about 75% of those with spinal cord injuries.
- Leading causes of spinal cord injury:
- motor vehicle accidents: 44%
- acts of violence: 24%
- falls: 22%
- sports: 8%
- other: 2%
People with paraplegia generally have no difficulty accessing web content. Those with quadriplegia, however, may have significant difficulties, depending on the type and severity of the injury. The condition can make it difficult or impossible to manipulate a mouse or type on a keyboard. However, assistive technologies are available to map users' abilities to their hardware.
Loss or damage of limb(s)
 Someone who can use one hand can use the Internet without too much difficulty, with a one-handed keyboard. Someone who has lost both limbs will use other technologies and devices like head wands, mouth sticks, voice recognition software, etc.
Someone who can use one hand can use the Internet without too much difficulty, with a one-handed keyboard. Someone who has lost both limbs will use other technologies and devices like head wands, mouth sticks, voice recognition software, etc.
Diseases and Congenital Conditions
Cerebral palsy
 Cerebral palsy is a brain injury causing decreased muscle control. The condition usually occurs during fetal development or shortly after birth. Characteristics include muscle tightness or spasms, involuntary movement, impaired speech, and occasionally paralysis.
Cerebral palsy is a brain injury causing decreased muscle control. The condition usually occurs during fetal development or shortly after birth. Characteristics include muscle tightness or spasms, involuntary movement, impaired speech, and occasionally paralysis.
In computer use, the condition primarily interferes with dexterity in using a mouse. Using a keyboard—or an adaptive keyboard—is still possible, albeit with some difficulty.
Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a genetic disorder in which the genes for muscle proteins are damaged, causing progressive degeneration of the muscles. It can affect people at any age, but is most common in children. Assistive technologies depend on the user's range of abilities, and include head wands, mouth sticks, adaptive keyboards, voice recognition software, etc.
Multiple sclerosis
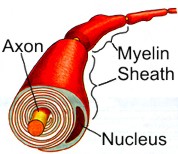 Multiple sclerosis (MS) erodes the myelin (a layer of fatty tissue which surrounds nerve fibers), blocking nerve fibers from delivering signals from the central nervous system to the muscles of the body. Effects include tremors, weakness, numbness, unstable walking, spasticity, slurred speech, muscle stiffness, impaired memory, and occasionally paralysis. Not all individuals experience all symptoms, and an individual may experience different symptoms over time. The types of assistive technologies and devices are the same as for other motor disabilities.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) erodes the myelin (a layer of fatty tissue which surrounds nerve fibers), blocking nerve fibers from delivering signals from the central nervous system to the muscles of the body. Effects include tremors, weakness, numbness, unstable walking, spasticity, slurred speech, muscle stiffness, impaired memory, and occasionally paralysis. Not all individuals experience all symptoms, and an individual may experience different symptoms over time. The types of assistive technologies and devices are the same as for other motor disabilities.
Spina bifida
 Spina bifida is a congenital condition leading to motor difficulties and possibly paralysis. In some cases, fluid can accumulate in and damage the brain. Some individuals experience learning and language difficulties as a result.
Spina bifida is a congenital condition leading to motor difficulties and possibly paralysis. In some cases, fluid can accumulate in and damage the brain. Some individuals experience learning and language difficulties as a result.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as "Lou Gehrig's Disease," is a degenerative disease that prevents neurons from sending impulses to the muscles. The muscles weaken over time, impacting dexterity in operating a mouse or keyboard, and the condition may eventually affect the muscles required for breathing, resulting in death. Symptoms include slowness in either movement or speech.
Arthritis
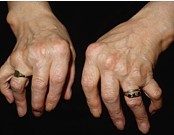 Arthritis pain can interfere with the fine motor control necessary to use a keyboard or use a mouse, touchpad, or mobile device to click small links or buttons. Depending on the user's range of comfort, a user may use a trackball mouse, voice recognition software, foot pedals, or other technologies. Joint pain can cause fatigue, limiting the amount of time that the person is willing to spend on a computer maneuvering a mouse and typing on a keyboard.
Arthritis pain can interfere with the fine motor control necessary to use a keyboard or use a mouse, touchpad, or mobile device to click small links or buttons. Depending on the user's range of comfort, a user may use a trackball mouse, voice recognition software, foot pedals, or other technologies. Joint pain can cause fatigue, limiting the amount of time that the person is willing to spend on a computer maneuvering a mouse and typing on a keyboard.
Parkinson's disease
 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a disorder of the central nervous system that causes uncontrollable tremors and/or rigidity in the muscles. The condition can significantly impede mouse and keyboard use. Occasionally the voice is affected as well, to the point that voice recognition software is not an option.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a disorder of the central nervous system that causes uncontrollable tremors and/or rigidity in the muscles. The condition can significantly impede mouse and keyboard use. Occasionally the voice is affected as well, to the point that voice recognition software is not an option.
Essential tremor
Like Parkinson's Disease, essential tremor (ET) is a nerve disorder that can result in uncontrollable tremors. Essential tremor most frequently affects the upper body, such as the hands, arms, head, and larynx (which impacts the voice).
Key Concepts
| Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Users may not be able to use the mouse. | Ensure all functions are available to both mouse/touchpad and keyboard users (try Tabbing from link to link). |
| Users may not be able to control the mouse or the keyboard well. | Ensure forms are error-tolerant (e.g., ask "are you sure you want to delete this file?"). Create sufficiently large links and buttons that remain in a static position. Allow users to remap or disable single key shortcuts. |
| Users may be using voice-activated software. | Voice-activated software can replicate mouse movement, but not as efficiently as keyboard functionality. Ensure all functions are available from the keyboard. Provide descriptive link and button text. |
| Users may become fatigued when using adaptive technologies. | Provide a method for skipping over long lists of links or other lengthy content. |
| Users may not be able to physically interact with their hardware device | Ensure content works in both horizontal or vertical orientation. Do not rely on motion actuation (such as shaking or panning the device) or pointer gestures (such as swiping or dragging). |
