Word 2010 for Windows
Creating Accessible Documents
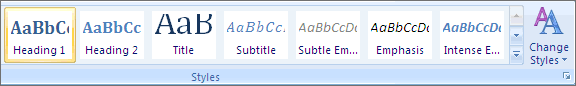
Creating and Editing Headings
- Select the tab from the ribbon.
- In your document, select the text to convert to a heading.
- Click on the appropriate heading level in the in-ribbon gallery; e.g., .
- Headings 1, 2, or 3 can also be assigned using Control + Alt + 1, 2, or 3, respectively.
Notes
Word documents with a true heading structure provide at least two benefits:
- The document retains this structure when correctly exported to HTML or PDF.
- The document's readability is increased for all users.
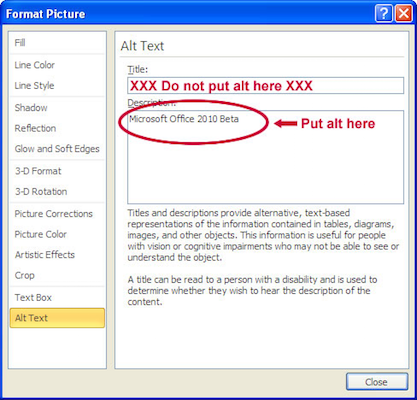
Adding Alternative Text
- Right-click on the image and select . A dialog box will appear.

- Select the option in the sidebar. Enter the appropriate alternative text in the field, NOT the field.
Creating Tables
- Use the command to create a table.
- If your table has a column header(s), right click on the first row in the table and select .
Important
Do NOT create tables "by hand" with spaces or the Tab key.
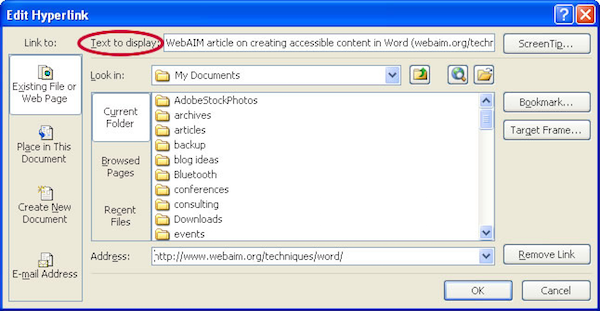
Editing Hyperlinks
- Select a hyperlink, right-click, and select or Ctrl + K.
- Change the text in the field to a more meaningful description.
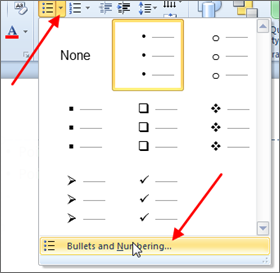
Creating Lists
- Select the tab on the ribbon.
- Select the or menu from the group.
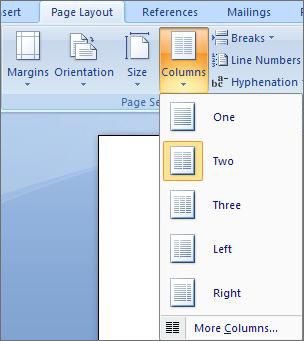
Creating Columns
- Select the tab on the ribbon.
- Select in the group.
Using the Accessibility Checker
- Select .
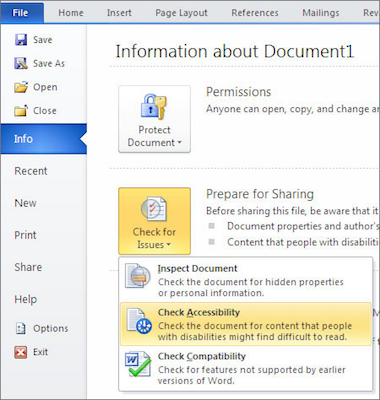
- The checker presents accessibility errors, warnings, and tips for making repairs.
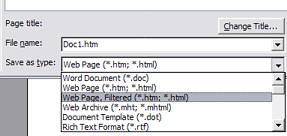
Saving as HTML
- Select the Word logo in the upper-left corner and then select .
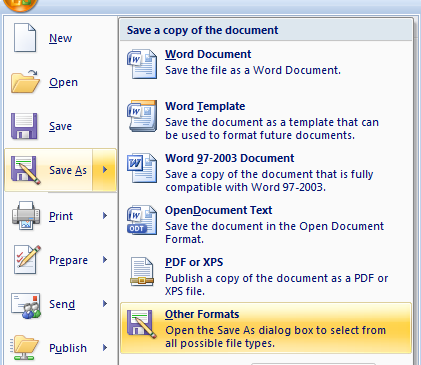
- Choose one of two options for exporting to HTML from the drop-down menu:
Converting to PDF
Users can create PDF files with the Adobe Acrobat add-in (recommended), or by using Word to save the document as a PDF file.
Adobe Acrobat Add-in
To export a PDF, select from the Acrobat ribbon:
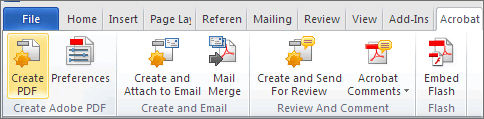
OR
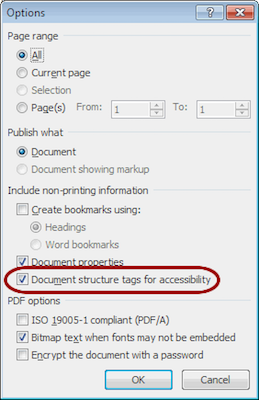
- Select .
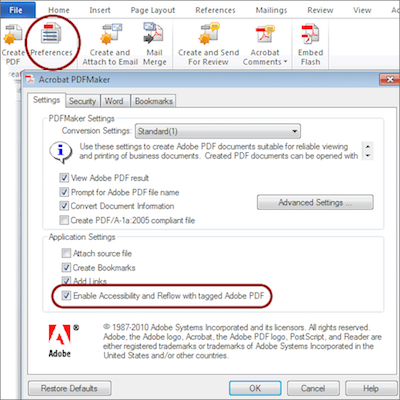
- Double-check that the proper are enabled in Word. You only need do this once:
- Select from the Acrobat ribbon.
- Ensure that the setting is checked in the dialog.
Saving to PDF with Word
Accessible PDF files can be created without installing the Adobe Acrobat add-in:
- Select .
- Under , select .
- Before saving, select and ensure that the option is selected.